
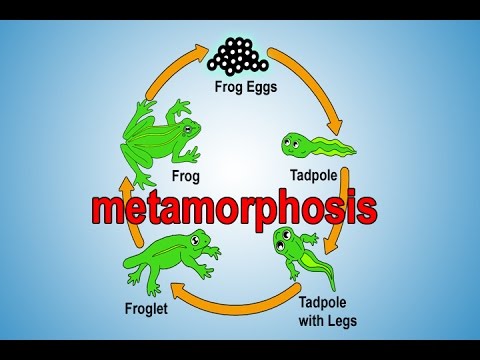
The life cycle of a frog consists of three stages: egg, larva, and adult.A few species are more active and follow in pursuit of their prey. Many frogs wait for their prey to come within range and then lunge after them. Some species also feed on small animals such as birds, mice, and snakes. Frogs feed on feed on insects and other invertebrates. Some species lack these long muscular back limbs and instead have legs better adapted to climbing, swimming, or even gliding. Such leaping is rarely used for normal locomotion but instead provides frogs with a way of escaping predators. Many frogs have large, muscular back limbs that enable them to launch themselves into the air.


The feet of frogs varies depending on their habitat. Frogs have four digits on their front feet and five on their rear feet.The term frog is used to refer to anuran species that have smooth, moist skin. In general, the term toad is used to apply to anuran species that have rough, warty skin. The terms "frog" and "toad" are informal and do not reflect any underlying taxonomic differences. There is no taxonomic distinction between frogs and toads.Of the approximately 6,000 species of amphibians, about 4,380 belong to the Order Anura. Frogs and toads, also referred to as anurans, represent the largest of the three amphibian groups. Newts and salamanders (Order Caudata), Caecilians (Order Gymnopiona), and frogs and toads (Order Anura). Frogs belong to the Order Anura, the largest of the three groups of amphibians.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
